The Prime Minister’s Council on Climate Change has included a new Mission on Climate Change and Health. A National Expert Group on Climate Change and Health has been constituted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare to address the issues related to adverse effects of climate change on human health.
According to the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, there is increasing concern in India over the effects of climate change on human health. Climate change affects the social and environmental determinants of health and weather events such as storms, floods, cyclones amplify the spread of vector-borne diseases, and the spread of food- and water-borne diseases.

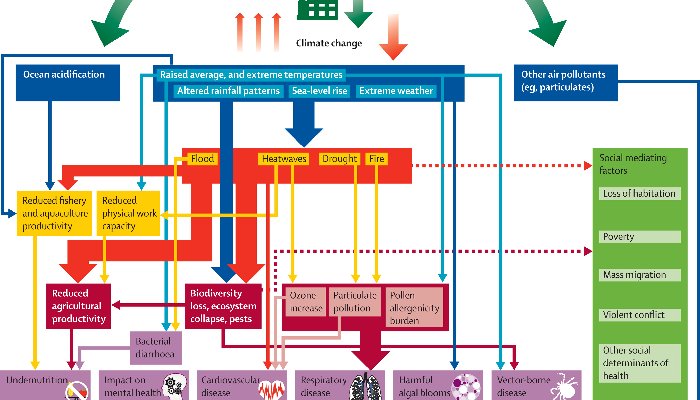
There are complex interactions between both causes and effects. Ecological processes, such as impacts on biodiversity and changes in disease vectors, and social dynamics, can amplify these risks. Graphic: Lancet
Work under this new mission is expected to complement running initiatives such as the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS). This programme focuses on prevention through awareness generation, behavior and life-style changes, early diagnosis and treatment of persons with high levels of risk factors and their referral to higher facilities for appropriate management. Funding is provided for human resources, infrastructure, early screening, and treatment as well as for Information, Education & Communication (IEC) activities.
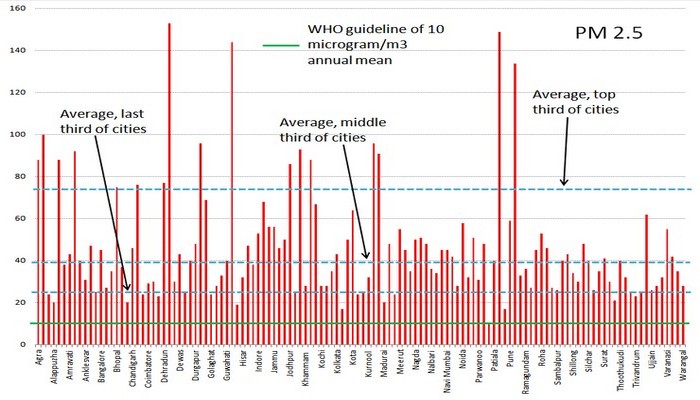
India and China suffer over USD 1.89 trillion annually in terms of the value of lives lost and ill health caused from air pollution, according to a major recent report which has underlined how climate change threatens to undermine half a century of progress in global health.

An overview of the links between greenhouse gas emissions, climate change, and health. Social responses also ameliorate some risks through adaptive actions. Graphic: Lancet
The analysis by the Lancet Commission on Health and Climate Change concluded that the benefits to health resulting from slashing fossil fuel use are so large that tackling global warming also presents the greatest global opportunity to improve people’s health in the 21st century. The Commission’s work was supported by the UN World Health Organisation.
The current trajectory, of average global temperature warming by 4 Celsius has very serious and potentially catastrophic effects for human health and human survival. The Commission said this must be seen as a medical emergency. The comprehensive analysis sets out the direct risks to health, including heatwaves, floods and droughts, and indirect – but no less deadly – risks, including air pollution, spreading diseases, famines and mental ill-health. A rapid phase-out of coal from the global energy mix is among the commission’s top recommendations, given the millions of premature deaths from air pollution this would prevent.
“The effects of climate change are being felt today, and future projections represent an unacceptably high and potentially catastrophic risk to human health,” said the report. “The implications of climate change for a global population of 9 billion people threatens to undermine the last half century of gains in development and global health. The direct effects of climate change include increased heat stress, floods, drought, and increased frequency of intense storms, with the indirect threatening population health through adverse changes in air pollution, the spread of disease vectors, food insecurity and under-nutrition, displacement, and mental ill health.”