The initial climate action pledges made by countries, and submitted to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), called Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs), have been analysed and reviewed by a group of 17 international civil society organisations. These findings have been released in a report, ‘Fair Shares: A Civil Society Equity Review of INDCs’.
INDCs refer to Intended Nationally Determined Contributions, the official name of the UNFCCC for the climate targets and actions which a majority of countries submitted on or before October 1, the deadline set by the UNFCCC. They are commonly referred to as “national climate targets/actions” or “pledges”. They are referred to as the initial offers of countries in terms of responding to climate change, and as the building blocks of the new global climate agreement, which is set to be finalized at the upcoming Paris climate conference. The current INDCs will be implemented from 2020 to 2025 or 2030.
The assessment includes INDCs covering 145 countries and some 80 percent of current global emissions. This review is different because it uses not only a science-based assessment of the necessary global level of climate action, but also uses widely accepted notions of equity to present fair shares of the necessary effort for each country. The equity and fair shares standards are anchored on the UNFCCC’s core principles of “common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities” and the “right to sustainable development”. The equity and fair shares standards used in this review take into account a range of interpretations of these principles. The group of international civil society organisations has said that the principles of equity and fair shares can be defined and quantified robustly, rigorously, transparently and scientifically, while accounting for differences of perspectives.
This review has said: “All countries should undertake their fair share of the global effort to tackle climate change. Each country’s fair share is based on its historical responsibility and capacity. Some countries have already emitted a great deal for a long time, contributing to warming that is happening already, and they thrive from the infrastructure and institutions they have been able to set up because of this. Some countries have much higher capacity to act than others, due to their higher income and wealth, level of development and access to technologies.”
This review is important because if the INDCs are not reviewed using a global carbon budget based on the science and widely held notions of equity, we will not be able to determine if each country committed its fair share of climate action. Equity and fairness are vital to unlocking cooperation, because – as the IPCC concluded in its most recent report – agreements that are seen to be fair are more likely to actually work. We will also not know if they are enough collectively to stave off dangerous global warming. The review sets a basis to demand higher ambition from each countries in Paris and beyond.
The review shows that the INDC commitments will likely lead the world to a devastating 3°C or more warming above pre-industrial levels. The current INDCs amount to barely half of the emissions cuts required by 2030.
Moreover, the INDCs submitted by all major developed countries fall well short of their fair shares. From the list of countries highlighted in the report, Russia’s INDC represents zero contribution towards committing its fair share. Japan’s represents about a tenth, the United States’ about a fifth, and the European Union’s just over a fifth of its fair share.
Most developed countries have fair shares that are already too large to fulfill exclusively within their borders, which is why there is a need for them to provide additional resources for developing countries to do more than their fair share, particularly through finance, technology, and capacity-building. However, there remains a striking lack of clear financial commitments from developed countries.
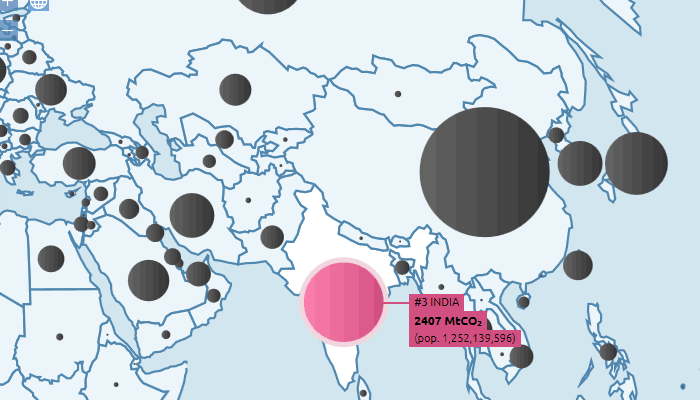
On the other hand, the majority of developing countries’ mitigation pledges exceed or broadly meet their fair share, including Kenya, the Marshall Islands, China, Indonesia, and India. Brazil’s INDC represents slightly more than two thirds of its fair share.
The question is: can developing countries with the largest rising emissions, such as China and Indonesia, now sit back because they have met their fair share? While the report clearly shows that the onus is on developed countries to commit more emissions cuts and financing, by no means does it give a free pass to developing countries. Our primary call is for each country – developing and developed – to do all it can in terms of climate action, working even to surpass its fair share.
What must therefore be done to close the emissions gap? The Paris COP21 agreement must ensure that domestic commitments and global targets alike are set in accordance with science and equity. It must also include a strong mechanism to increase the ambition of INDCs before their implementation in 2020, and every five years thereafter. Developed countries must make substantial new commitments to finance mitigation, adaptation, and loss and damage in developing countries for a fully equitable climate agreement. Finally, countries must scale up action for sustainable energy transformation.
[The group: ActionAid International, Asian Peoples’ Movement on Debt and Development, Climate Action Network South Asia, CARE International, Center for International Environmental Law, Christian Aid, CIDSE, Climate Action Network Latin America, Friends of the Earth International, International Trade Union Confederation, LDC Watch International, Oxfam, Pan African Climate Justice Alliance, SUSWATCH Latin America, Third World Network, What Next Forum, and WWF International. The Climate Equity Reference Project, an initiative of EcoEquity and the Stockholm Environment Institute, provided analytical support. It is also supported by numerous social movements, networks, and other civil society groups in the international, regional, and national levels.]


 The Government of India has said that the country’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) are balanced and comprehensive. In official statements, the government said that INDCs include reductions in the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33 to 35 per cent by 2030 from 2005 level and to create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030. India has also decided to anchor a global solar alliance, INSPA (International Agency for Solar Policy & Application), of all countries located in between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
The Government of India has said that the country’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) are balanced and comprehensive. In official statements, the government said that INDCs include reductions in the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33 to 35 per cent by 2030 from 2005 level and to create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030. India has also decided to anchor a global solar alliance, INSPA (International Agency for Solar Policy & Application), of all countries located in between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn. The INDCs centre around India’s policies and programmes on promotion of clean energy, especially renewable energ
The INDCs centre around India’s policies and programmes on promotion of clean energy, especially renewable energ
 The INDCs outline the post-2020 climate actions they intend to take under a new international agreement. The INDCs document is prepared with a view to taking forward the Prime Minister’s vision of a sustainable lifestyle and climate justice to protect the poor and vulnerable from adverse impacts of climate change. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change adopted an inclusive process for preparation of India’s INDCs. It held stakeholder consultations with the specific involvement of the key Ministries and State Governments. Interactions were also held with civil society organisations, thinktanks and technical & academic institutions of eminence. The Ministry had commissioned Greenhouse Gas (GHG) modeling studies for projections of GHG emissions till 2050 with a decadal gap. The gist of all these consultations & studies were taken on board before submitting India’s INDCs. The government zeroed-in on a set of contributions which are comprehensive, balanced, equitable and pragmatic and addresses all the elements including Adaptation, Mitigation, Finance, Technology Transfer, Capacity Building and Transparency in Action and Support.
The INDCs outline the post-2020 climate actions they intend to take under a new international agreement. The INDCs document is prepared with a view to taking forward the Prime Minister’s vision of a sustainable lifestyle and climate justice to protect the poor and vulnerable from adverse impacts of climate change. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change adopted an inclusive process for preparation of India’s INDCs. It held stakeholder consultations with the specific involvement of the key Ministries and State Governments. Interactions were also held with civil society organisations, thinktanks and technical & academic institutions of eminence. The Ministry had commissioned Greenhouse Gas (GHG) modeling studies for projections of GHG emissions till 2050 with a decadal gap. The gist of all these consultations & studies were taken on board before submitting India’s INDCs. The government zeroed-in on a set of contributions which are comprehensive, balanced, equitable and pragmatic and addresses all the elements including Adaptation, Mitigation, Finance, Technology Transfer, Capacity Building and Transparency in Action and Support. Planned actions and economic reforms have contributed positively to the rapidly declining growth rate of energy intensity in India.
Planned actions and economic reforms have contributed positively to the rapidly declining growth rate of energy intensity in India.  India has adopted several ambitious measures for clean and renewable energy, energy efficiency in various sectors of industries, achieving lower emission intensity in the automobile and transport sector, non-fossil based electricity generation and building sector based on energy conservation. Thrust on renewable energy, promotion of clean energy, enhancing energy efficiency, developing climate resilient urban centres and sustainable green transportation network are some of the measures for achieving this goal.
India has adopted several ambitious measures for clean and renewable energy, energy efficiency in various sectors of industries, achieving lower emission intensity in the automobile and transport sector, non-fossil based electricity generation and building sector based on energy conservation. Thrust on renewable energy, promotion of clean energy, enhancing energy efficiency, developing climate resilient urban centres and sustainable green transportation network are some of the measures for achieving this goal. Solar power in India is poised to grow significantly with Solar Mission as a major initiative of the Government of India. A scheme for development of 25 Solar Parks, Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects, canal top solar projects and one hundred thousand solar pumps for farmers is at different stages of implementation. The Government’s goal of ‘Electricity for All’ is sought to be achieved by the above programs that would require huge investments, infusion of new technology, availability of nuclear fuel and international support.
Solar power in India is poised to grow significantly with Solar Mission as a major initiative of the Government of India. A scheme for development of 25 Solar Parks, Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects, canal top solar projects and one hundred thousand solar pumps for farmers is at different stages of implementation. The Government’s goal of ‘Electricity for All’ is sought to be achieved by the above programs that would require huge investments, infusion of new technology, availability of nuclear fuel and international support. The energy efficiency of thermal power plants will be systematically and statutorily improved. Over one million medium and small enterprises will be involved in the Zero Defect Zero Effect Scheme to improve their quality, energy efficiency, enhance resource efficiency, pollution control, waste management and use of renewable energy.
The energy efficiency of thermal power plants will be systematically and statutorily improved. Over one million medium and small enterprises will be involved in the Zero Defect Zero Effect Scheme to improve their quality, energy efficiency, enhance resource efficiency, pollution control, waste management and use of renewable energy. The range of ecosystem goods and services provided by forests include carbon sequestration and storage. Despite the significant opportunity costs, India is one of the few countries where forest and tree cover has increased in recent years and the total forest and tree cover amounts to 24% percent of the geographical area of the country. Over the past two decades progressive national forestry legislations and policies of India have transformed India’s forests into a net sink of CO2. With its focus on sustainable forest management, afforestation and regulating diversion of forest land for non-forest purpose, India plans to increase its carbon stock. Government of India’s long term goal is to increase its forest cover through a planned afforestation drive which includes number of programmes and initiatives like Green India Mission, green highways policy, financial incentive for forests, plantation along rivers, REDD-Plus & Other Policies and Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority
The range of ecosystem goods and services provided by forests include carbon sequestration and storage. Despite the significant opportunity costs, India is one of the few countries where forest and tree cover has increased in recent years and the total forest and tree cover amounts to 24% percent of the geographical area of the country. Over the past two decades progressive national forestry legislations and policies of India have transformed India’s forests into a net sink of CO2. With its focus on sustainable forest management, afforestation and regulating diversion of forest land for non-forest purpose, India plans to increase its carbon stock. Government of India’s long term goal is to increase its forest cover through a planned afforestation drive which includes number of programmes and initiatives like Green India Mission, green highways policy, financial incentive for forests, plantation along rivers, REDD-Plus & Other Policies and Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority