We wish Insat-3D a very happy second birthday and warmly congratulate the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) on this anniversary.
Insat-3D completed two successful years in orbit on 26 July 2015. The Advanced Weather Satellite is designed for enhanced meteorological observations and monitoring of land and ocean surfaces for weather forecasting and disaster warning. Insat-3D is the first Indian geostationary satellite equipped with instruments that provide frequent good quality atmospheric profiles (temperature, humidity) over the Indian landmass and adjoining areas.
Thanks to the coordination between ISRO and the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), we at India Climate Portal make heavy and frequent use of the many observational products, all free in the public domain, to inform you about weather and climate.
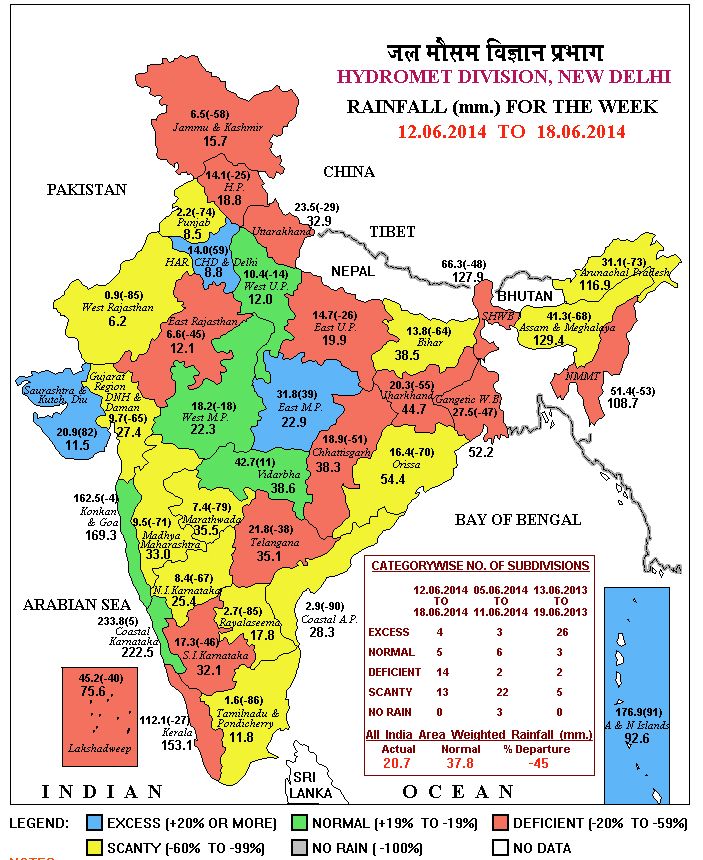
 Insat-3D provides us high quality observations for monitoring and predicting of weather events as well as studying our climate. The advanced ‘Imager’ and ‘Sounder’ on the satellite provide a wide range of atmospheric products such as cloud coverage images, atmospheric winds, sea and land surface temperatures, humidity, quantitative rainfall, earth’s radiation, atmospheric profiles, ozone, atmospheric stability parameters, fog, snow, aerosols. These products are immensely helpful in monitoring day-to-day weather and prediction of extreme events like tropical cyclone, thunderstorm, cloud burst and heat waves.
Insat-3D provides us high quality observations for monitoring and predicting of weather events as well as studying our climate. The advanced ‘Imager’ and ‘Sounder’ on the satellite provide a wide range of atmospheric products such as cloud coverage images, atmospheric winds, sea and land surface temperatures, humidity, quantitative rainfall, earth’s radiation, atmospheric profiles, ozone, atmospheric stability parameters, fog, snow, aerosols. These products are immensely helpful in monitoring day-to-day weather and prediction of extreme events like tropical cyclone, thunderstorm, cloud burst and heat waves.
The ‘Imager’ has completed 25,733 scans and ‘Sounder’ has completed 14,866 scans until the end of May 2015. The Insat-3D spacecraft was dedicated to the country at the National Satellite Meteorological Center (NCMC), India Meteorological Department (IMD), New Delhi on 15 January 2014. An indigenously designed and developed Insat-3D Meteorological Data Processing System processes all data transmitted by the Imager and Sounder. The data archival and dissemination is through IMD, New Delhi and the Meteorological and Oceanographic Satellite Data Archival Centre (MOSDAC, at Space Applications Centre, Ahmedabad).
A number of Insat-3D observations and derived products are being used in models operated by national weather prediction agencies like the IMD and the National Centre for Medium Range Weather Prediction (NCMRWF). Moreover, the European Centrer for Medium range Weather Forecast (ECMWF) and the United Kingdom Meteorological Office (UKMET) plan to use Insat-3D derived data in their global models.
As always, the ISRO family, staff, engineers, scientists and technicians excel at what they do best. In tandem with the committed and dilligent meteorologists of the IMD, they have given us free information, as good as the best the world can offer, so that we understand our Bharat better.