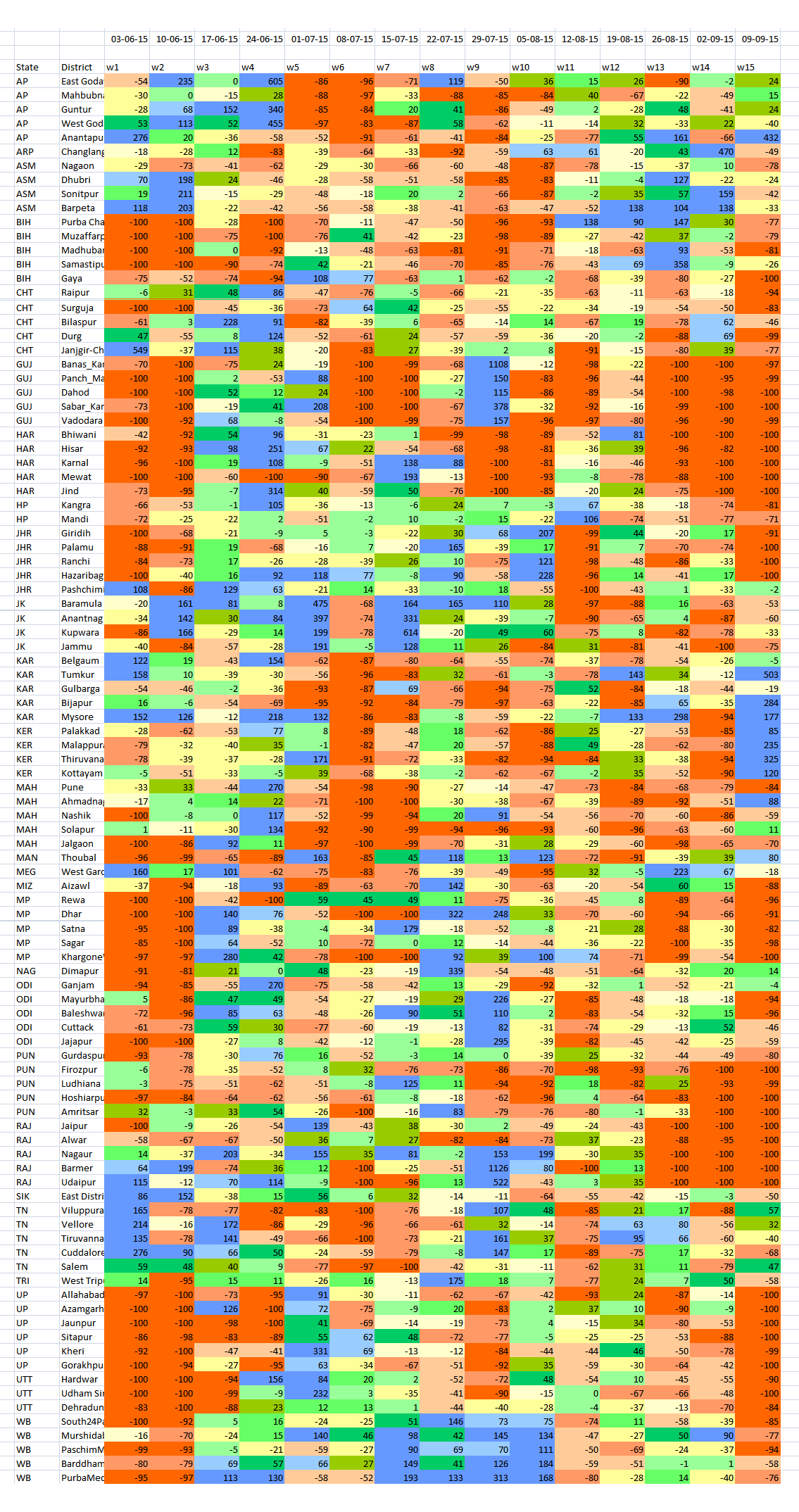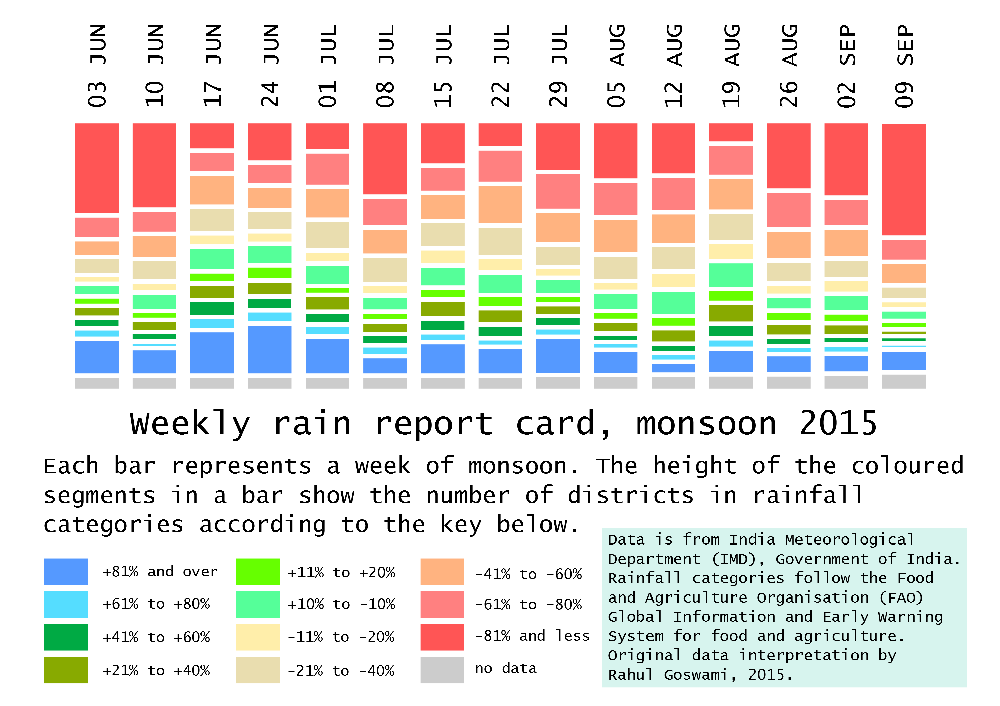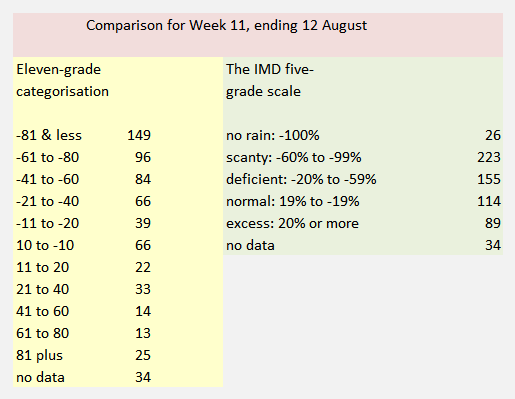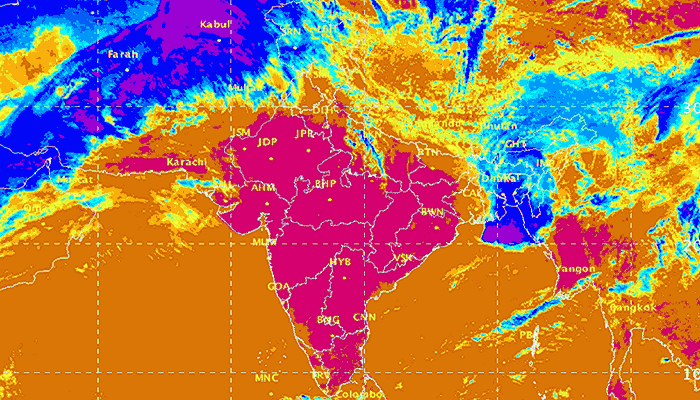
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has issued its forecast for the 2016 hot weather season (April to June). The forecast shows that during the 2016 hot weather season, temperatures (mean, maximum and minimum) in all the sub-divisions are likely to be above normal. All the temperatures (maximum, minimum and mean) of most of the subdivisions from northwest India, Kerala from south India and Vidharbha from Central India are likely to be above normal by 1.0° C or more. Read the full forecast document here (pdf).
The season averaged maximum temperatures of coastal Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Assam and Meghalaya, sub-Himalayan west Bengal and Sikkim, and NMMT – Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura – are likely to be warmer by 0.5° C and that of the remaining subdivisions are likely to warmer than normal by 0.5° to 1° C. The season averaged minimum temperatures of sub-Himalayan west Bengal and Sikkim, and NMMT are likely to be warmer than normal by <0.5° C and that of the remaining subdivisions are likely to warmer than normal by 0.5° to 1° C.
There is also a high probability (76%) of maximum temperatures in the core heat wave zone during the 2016 hot weather season to be above normal. The core heat wave zone covers the states of Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, the National Capital Territory and Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha and Telengana and the meteorological sub-divisions of Marathwada, Vidharbha, Madhya Maharashtra and coastal Andhra Pradesh. This in turn suggests high probability of moderate and severe heat wave conditions in the core heat wave zone during the hot weather season.
From this season, the IMD will also provide extended range forecasts (five–day averaged forecasts for the next 15 days) of heat wave conditions over the country. This will be based on the Dynamical Extended Range Forecasting System developed by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune. The forecast will consist of the probability of occurrence of hot days, heat waves and severe heat waves for the next 15 days updated every fifth day from 1 April, 2016. The forecasts will be available on the IMD website.










 The Government of India has said that the country’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) are balanced and comprehensive. In official statements, the government said that INDCs include reductions in the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33 to 35 per cent by 2030 from 2005 level and to create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030. India has also decided to anchor a global solar alliance, INSPA (International Agency for Solar Policy & Application), of all countries located in between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
The Government of India has said that the country’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs) are balanced and comprehensive. In official statements, the government said that INDCs include reductions in the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33 to 35 per cent by 2030 from 2005 level and to create an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by 2030. India has also decided to anchor a global solar alliance, INSPA (International Agency for Solar Policy & Application), of all countries located in between Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn. The INDCs centre around India’s policies and programmes on promotion of clean energy, especially renewable energ
The INDCs centre around India’s policies and programmes on promotion of clean energy, especially renewable energ
 The INDCs outline the post-2020 climate actions they intend to take under a new international agreement. The INDCs document is prepared with a view to taking forward the Prime Minister’s vision of a sustainable lifestyle and climate justice to protect the poor and vulnerable from adverse impacts of climate change. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change adopted an inclusive process for preparation of India’s INDCs. It held stakeholder consultations with the specific involvement of the key Ministries and State Governments. Interactions were also held with civil society organisations, thinktanks and technical & academic institutions of eminence. The Ministry had commissioned Greenhouse Gas (GHG) modeling studies for projections of GHG emissions till 2050 with a decadal gap. The gist of all these consultations & studies were taken on board before submitting India’s INDCs. The government zeroed-in on a set of contributions which are comprehensive, balanced, equitable and pragmatic and addresses all the elements including Adaptation, Mitigation, Finance, Technology Transfer, Capacity Building and Transparency in Action and Support.
The INDCs outline the post-2020 climate actions they intend to take under a new international agreement. The INDCs document is prepared with a view to taking forward the Prime Minister’s vision of a sustainable lifestyle and climate justice to protect the poor and vulnerable from adverse impacts of climate change. Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change adopted an inclusive process for preparation of India’s INDCs. It held stakeholder consultations with the specific involvement of the key Ministries and State Governments. Interactions were also held with civil society organisations, thinktanks and technical & academic institutions of eminence. The Ministry had commissioned Greenhouse Gas (GHG) modeling studies for projections of GHG emissions till 2050 with a decadal gap. The gist of all these consultations & studies were taken on board before submitting India’s INDCs. The government zeroed-in on a set of contributions which are comprehensive, balanced, equitable and pragmatic and addresses all the elements including Adaptation, Mitigation, Finance, Technology Transfer, Capacity Building and Transparency in Action and Support. Planned actions and economic reforms have contributed positively to the rapidly declining growth rate of energy intensity in India.
Planned actions and economic reforms have contributed positively to the rapidly declining growth rate of energy intensity in India.  India has adopted several ambitious measures for clean and renewable energy, energy efficiency in various sectors of industries, achieving lower emission intensity in the automobile and transport sector, non-fossil based electricity generation and building sector based on energy conservation. Thrust on renewable energy, promotion of clean energy, enhancing energy efficiency, developing climate resilient urban centres and sustainable green transportation network are some of the measures for achieving this goal.
India has adopted several ambitious measures for clean and renewable energy, energy efficiency in various sectors of industries, achieving lower emission intensity in the automobile and transport sector, non-fossil based electricity generation and building sector based on energy conservation. Thrust on renewable energy, promotion of clean energy, enhancing energy efficiency, developing climate resilient urban centres and sustainable green transportation network are some of the measures for achieving this goal. Solar power in India is poised to grow significantly with Solar Mission as a major initiative of the Government of India. A scheme for development of 25 Solar Parks, Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects, canal top solar projects and one hundred thousand solar pumps for farmers is at different stages of implementation. The Government’s goal of ‘Electricity for All’ is sought to be achieved by the above programs that would require huge investments, infusion of new technology, availability of nuclear fuel and international support.
Solar power in India is poised to grow significantly with Solar Mission as a major initiative of the Government of India. A scheme for development of 25 Solar Parks, Ultra Mega Solar Power Projects, canal top solar projects and one hundred thousand solar pumps for farmers is at different stages of implementation. The Government’s goal of ‘Electricity for All’ is sought to be achieved by the above programs that would require huge investments, infusion of new technology, availability of nuclear fuel and international support. The energy efficiency of thermal power plants will be systematically and statutorily improved. Over one million medium and small enterprises will be involved in the Zero Defect Zero Effect Scheme to improve their quality, energy efficiency, enhance resource efficiency, pollution control, waste management and use of renewable energy.
The energy efficiency of thermal power plants will be systematically and statutorily improved. Over one million medium and small enterprises will be involved in the Zero Defect Zero Effect Scheme to improve their quality, energy efficiency, enhance resource efficiency, pollution control, waste management and use of renewable energy. The range of ecosystem goods and services provided by forests include carbon sequestration and storage. Despite the significant opportunity costs, India is one of the few countries where forest and tree cover has increased in recent years and the total forest and tree cover amounts to 24% percent of the geographical area of the country. Over the past two decades progressive national forestry legislations and policies of India have transformed India’s forests into a net sink of CO2. With its focus on sustainable forest management, afforestation and regulating diversion of forest land for non-forest purpose, India plans to increase its carbon stock. Government of India’s long term goal is to increase its forest cover through a planned afforestation drive which includes number of programmes and initiatives like Green India Mission, green highways policy, financial incentive for forests, plantation along rivers, REDD-Plus & Other Policies and Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority
The range of ecosystem goods and services provided by forests include carbon sequestration and storage. Despite the significant opportunity costs, India is one of the few countries where forest and tree cover has increased in recent years and the total forest and tree cover amounts to 24% percent of the geographical area of the country. Over the past two decades progressive national forestry legislations and policies of India have transformed India’s forests into a net sink of CO2. With its focus on sustainable forest management, afforestation and regulating diversion of forest land for non-forest purpose, India plans to increase its carbon stock. Government of India’s long term goal is to increase its forest cover through a planned afforestation drive which includes number of programmes and initiatives like Green India Mission, green highways policy, financial incentive for forests, plantation along rivers, REDD-Plus & Other Policies and Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority