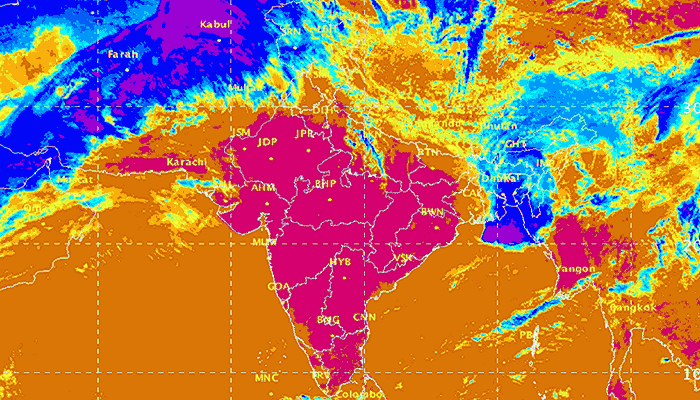
A large number of districts in south, peninsular, central and eastern India are experiencing dry and semi-arid conditions which will continue, and likely become worse, until the 2017 monsoon becomes active.
This list of districts is based on our re-working of the maps released weekly by the India Meteorological Department (Hydromet section in Pune), which show the district-level standardised precipitation index (or SPI). While this is not a drought or dryness index, the weekly SPI serves as a very reliable indicator of where water stress is occurring, and is therefore an invaluable aid for relief planning.

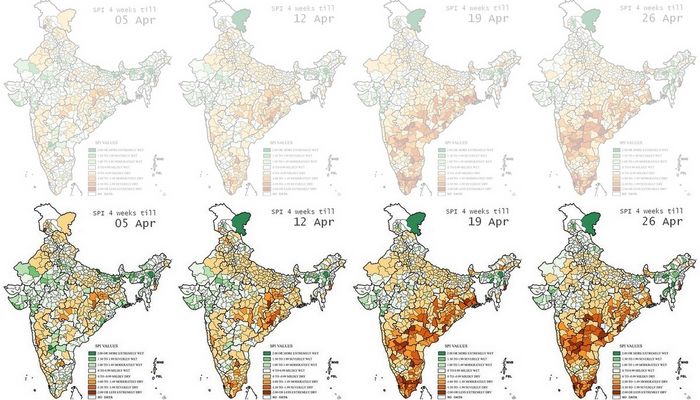
In this series of four maps, re-coloured by us to better display differences in SPI between regions and over time, the change in south India stands out.
Each map displays the SPI as a cumulative reading of the four weeks until the date given. That is why the change for any district – from ‘moderately dry’ to ‘severely dry’ for example – needs to be seen as having an immediate bearing on the available water, crop health and condition of forest and pasture for that district.
Based on the readings for 26 April 2017 this is the list of districts that need urgent attention.
Maharashtra: Gadchiroli, Chandrapur, Yavatmal, Kolhapur
Chhattisgarh (Raipur division): Gariaband, Raipur, Baloda Bazar
Odisha: Rayagada, Kandhamal, Angul, Cuttack
West Bengal: 24 Parganas North
Manipur: Chandel
Andhra Pradesh: Vizianagaram, Kurnool
Telengana (old district boundaries): Nizamabad, Karimnagar, Medak, Warangal, Khammam, Mahbubnagar
Karnataka: Bidar, Raichur, Bijapur, Bagalkot, Koppal, Gadag, Dharwad, Bellary, Shimoga
Tamil Nadu: Cuddalore, Nagapattinam, Tiruvarur, Thanjavur, Pudukkottai, Ramanathapuram, Toothukudi, Kaniyakumari, Theni, Coimbatore
Kerala: Malappuram, Thrissur, Ernakulam, Kottayam, Alapuzha