
The Central Water Commission, Ministry of Water Resources, Government of India, monitors every day the quantity of water stored (and used from) each of the 91 major reservoirs of the country. It issues a bulletin every week that gives the weekly storage position of these reservoirs – the volume of water, the level of water in the reservoir and the change from the last week, the change from the same date last year and from the average on this date of the last ten years.
The water storage capacity of these 91 reservoirs taken together is 157.799 billion cubic metres (bcm) which is estimated to be about 62% of the total water storage capacity (in other smaller dams and storage structures all over the country) that has been built and is being used, and which is approximately 253.38 bcm. Out of these 91 reservoirs, hydro-electric power stations (with a capacity of 60 megawatts and more) are attached to 37 reservoirs.
In this illustration by Indiaclimate, for the first time the total storage capacity of the 91 major reservoirs has been visually mapped to show reservoir, state and zone capacities relative to each other and the total.

These are the reservoirs with state, reservoir name and full reservoir level in billion cubic metres (bcm). For a good quality file that you can print, write to us.
South zone reservoirs (AP for Andhra Pradesh, TG for Telengana, APTG for Andhra Pradesh and Telegana together, KAR for Karnataka, TN for Tamil Nadu, KER for Kerala): AP, Somasila (1.994); TG, Sriramsagar (2.3); TG, Lower Manair (0.621); APTG, Srisailam (8.288); APTG, Nagarjuna Sagar (6.841); KAR, Krishnaraja Sagra (1.163); KAR, Tungabhadra (3.276); KAR, Ghataprabha (1.391); KAR, Bhadra (1.785); KAR, Linganamakki (4.294); KAR, Narayanpur (0.863); KAR, Malaprabha (Renuka) (0.972); KAR, Kabini (0.444); KAR, Hemavathy (0.927); KAR, Harangi (0.22); KAR, Supa (4.12); KAR, Vanivilas Sagar (0.802); KAR, Almatti (3.105); KAR, Gerusoppa (0.13); KER, Kallada (Parappar) (0.507); KER, Idamalayar (1.018); KER, Idukki (1.46); KER, Kakki (0.447); KER, Periyar (0.173); KER, Malapmuzha (0.224); TN, Lower Bhawani (0.792); TN, Mettur (Stanley) (2.647); TN, Vaigai (0.172); TN, Parambikulam (0.38); TN, Aliyar (0.095); TN, Sholayar (0.143). Total for 31 reservoirs 51.59 bcm
West zone reservoirs (GUJ for Gujarat, MAH for Maharashtra): GUJ, Ukai (6.615); GUJ, Sabarmati (Dharoi) (0.735); GUJ, Kadana (1.472); GUJ, Shetrunji (0.3); GUJ, Bhadar (0.188); GUJ, Damanaganga (0.502); GUJ, Dantiwada (0.399); GUJ, Panam (0.697); GUJ, Sardar Sarovar (1.566); GUJ, Karjan (0.523); MAH, Jayakwadi (Paithon) (2.171); MAH, Koyana (2.652); MAH, Bhima (Ujjani) (1.517); MAH, Isapur (0.965); MAH, Mula (0.609); MAH, Yeldari (0.809); MAH, Girna (0.524); MAH, Khadakvasla (0.056); MAH, Upper Vaitarna (0.331); MAH, Upper Tapi (0.255); MAH, Pench (Totaladoh) (1.091); MAH, Upper Wardha (0.564); MAH, Bhatsa (0.942); MAH, Dhom (0.331); MAH, Dudhganga (0.664); MAH, Manikdoh (Kukadi) (0.288); MAH, Bhandardara (0.304). Total for 27 reservoirs 27.07 bcm
East zone reservoirs (JHR for Jharkhand, ODI for Odisha, WB for West Bengal, TRI for Tripura): JHR, Tenughat (0.821); JHR, Maithon (0.471); JHR, Panchet Hill (0.184); JHR, Konar (0.176); JHR, Tilaiya (0.142); ODI, Hirakud (5.378); ODI, Balimela (2.676); ODI, Salanadi (0.558); ODI, Rengali (3.432); ODI, Machkund (Jalput) (0.893); ODI, Upper Kolab (0.935); ODI, Upper Indravati (1.456); WB, Mayurakshi (0.48); WB, Kangsabati (0.914); TRI, Gumti (0.312). Total for 15 reservoirs 18.83 bcm
Central zone reservoirs (UP for Uttar Pradesh, UTT for Uttarakhand, MP for Madhya Pradesh, CHT for Chhattisgarh): UP, Matatila (0.707); UP, Rihand (5.649); UTT, Ramganga (2.196); UTT, Tehri (2.615); MP, Gandhi Sagar (6.827); MP, Tawa (1.944); MP, Bargi (3.18); MP, Bansagar (5.166); MP, Indira Sagar (9.745); MP, Barna (0.456); CHT, Minimata Bangoi (3.046); CHT, Mahanadi (0.767). Total for 12 reservoirs 42.30 bcm
North zone reservoirs (HP for Himachal Pradesh, PUN for Punjab, RAJ for Rajasthan): HP, Gobind Sagar (Bhakra) (6.229); HP, Pong Dam (6.157); PUN, Thein (2.344); RAJ, Mahi Bajaj Sagar (1.711); RAJ, Jhakam (0.132); RAJ, Rana Pratap Sagar (1.436). Total for 6 reservoirs 18.01 bcm
 By the end of the first week of April 2017, the most current and reliable indicator for stored water in south India showed how dire the situation has become. And the South-West monsoon is still about eight weeks away. The weekly data sheet on the stored water quantities in the 91 major reservoirs of India, which is maintained and released by the Central Water Commission, has in the 6 April 2017 release shown the scale of the water emergency.
By the end of the first week of April 2017, the most current and reliable indicator for stored water in south India showed how dire the situation has become. And the South-West monsoon is still about eight weeks away. The weekly data sheet on the stored water quantities in the 91 major reservoirs of India, which is maintained and released by the Central Water Commission, has in the 6 April 2017 release shown the scale of the water emergency.

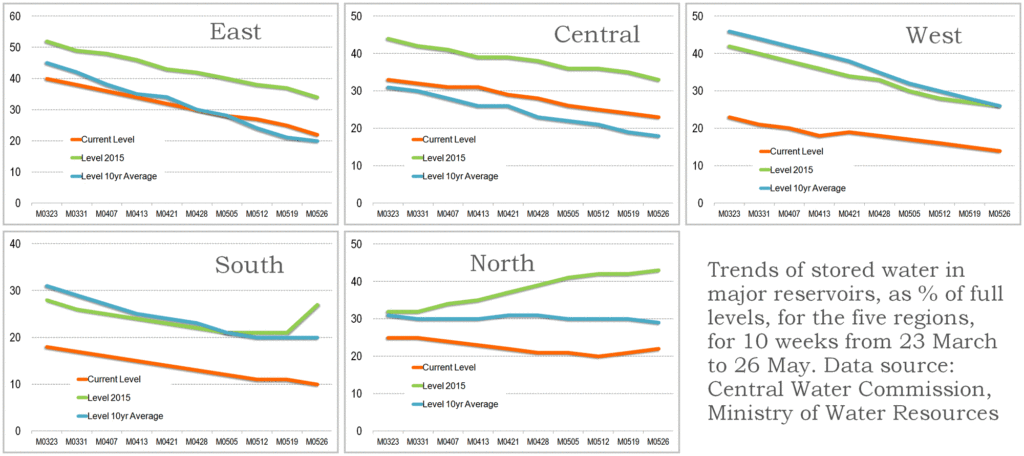



 Every week, the Central Water Commission releases to the public and to government departments the numbers that describe how much water is stored in 85 reservoirs in India. These are the reservoirs designated as nationally important, because of their roles in providing water for large irrigated command areas and for generating hydro-electric power (37 of these dams).
Every week, the Central Water Commission releases to the public and to government departments the numbers that describe how much water is stored in 85 reservoirs in India. These are the reservoirs designated as nationally important, because of their roles in providing water for large irrigated command areas and for generating hydro-electric power (37 of these dams).
