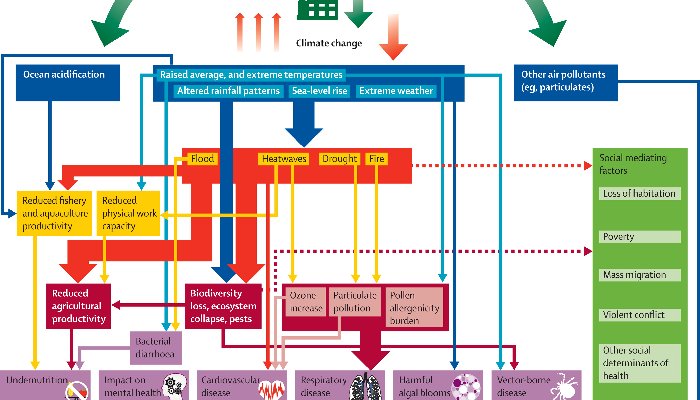
With two weeks of the June to September monsoon remaining in 2015, one of the end-of-season conclusions that the India Meteorological Department (IMD) has spoken of is that four out of ten districts in the country has had less rainfall than normal.
This overview is by itself alarming, but does not aid state governments and especially line ministries plan for coming months, particularly for agriculture and cultivation needs, water use, the mobilisation of resources for contingency measures, and to review the short- and medium-term objectives of development programmes.
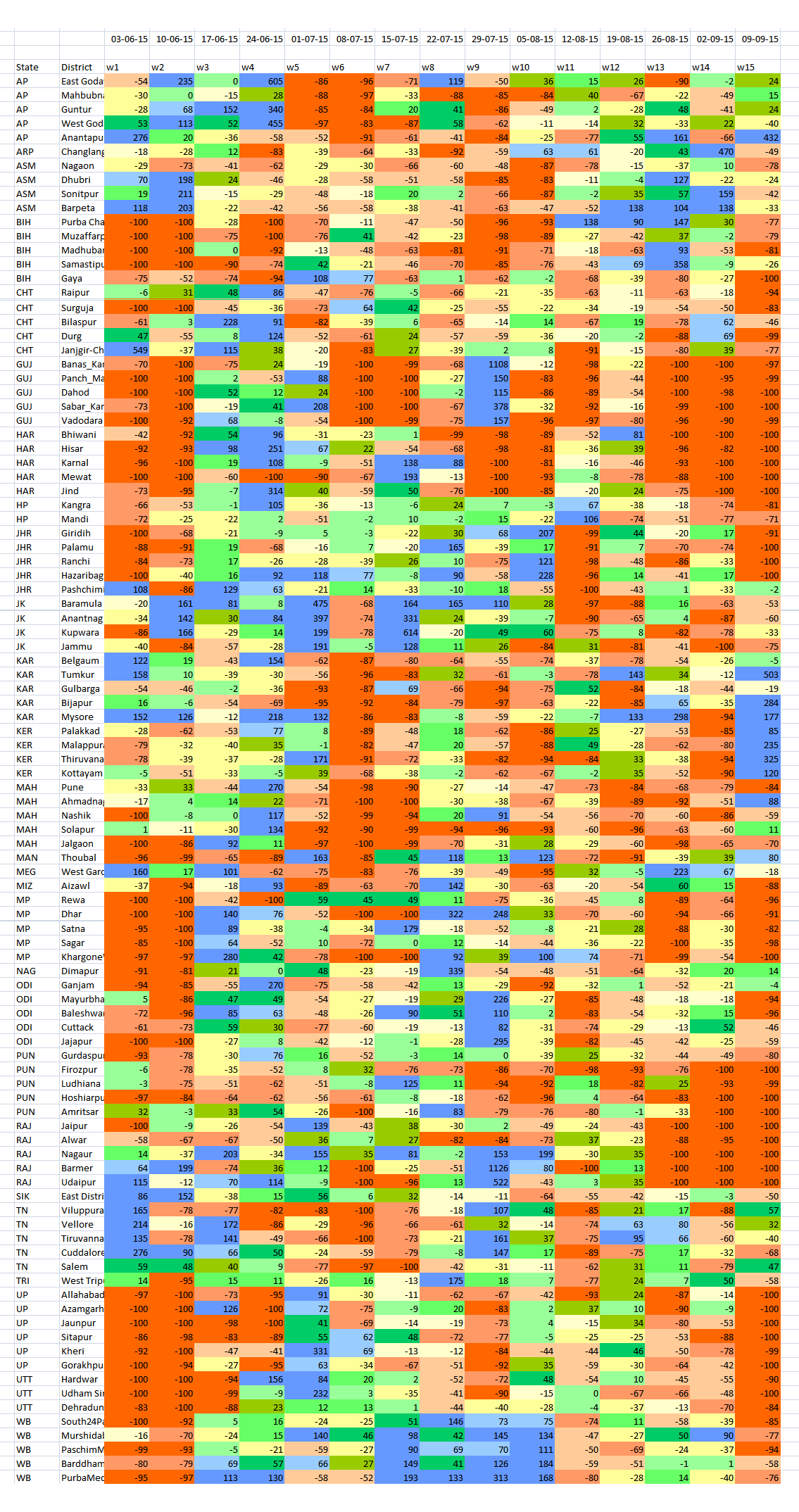 The detailed tabulation provided here is meant to provide guidance of where this may be done immediately – in the next two to four weeks – and how this can be done in future.
The detailed tabulation provided here is meant to provide guidance of where this may be done immediately – in the next two to four weeks – and how this can be done in future.
The table lists 100 districts each of which have readings 15 weeks of rainfall variation – the numbers are not rainfall in millimetres (mm) but the variation in per cent from the long-term normal for that district for that week. The colour codes for each district’s week cell are the same as those used for the new 11-grade rainfall categorisation.
The districts are chosen on the basis of the size of their rural populations (calculated for 2015). Thus Purba Champaran in Bihar, Bhiwani in Haryana, Rewa in Madhya Pradesh and Viluppuram in Tamil Nadu are the districts in those states with the largest rural populations.
In this way, the effect of rainfall variability, from Week 1 (which ended on 3 June) to Week 15 (which ended on 9 September), in the districts with the largest rural populations can be analysed. Because a large rural population is also a large agricultural population, the overall seasonal impact on that district’s agricultural output can also be inferred.
The distribution of the districts is: six from Uttar Pradesh; five each from Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Haryana, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal; four each from Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, and Kerala; three from Uttarakhand; two from Himachal Pradesh; one each from Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura.
Using the new 11-grade rainfall categorisation, a normal rainweek is one in which the rainfall is between +10% more and -10% less for that week. The overview for this group of 100 districts, only 11 have had five or more normal weeks of rain out of 15 weeks. In alarming contrast, there are 77 districts which have had three or fewer normal weeks of rain – that is, more than three-fourths of these most populous districts. Half the number (51 districts) have had two, one or no normal weeks of rain. And 22 of these districts have had only one or no normal weeks of rain.
From this group of 100 most populous (rural population) districts Gorakhpur in Uttar Pradesh and Nagaon in Assam have had the most deficit rainweeks, tallying 13, out of the 15 tabulated so far. There are ten districts which have had 12 deficit rainweeks out of 15 and they are (in decreasing order of rural population): Muzaffarpur (Bihar), Pune and Jalgaon (Maharashtra), Surguja (Chhattisgarh), Panch Mahals and Vadodara (Gujarat), Firozpur (Punjab), Thiruvananthapuram (Kerala), Hoshiarpur (Punjab) and Mewat (Haryana).
– Rahul Goswami