
Less rain for the remaining two months of the typical monsoon season of four months, but an overall season average that remains as it was forecast in June. This is the confusing monsoon update issued by the Earth System Science Organization (ESSO), the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) and the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
There are aspects of IMD’s treatment of the monsoon season that need correction in our view. One is the long range forecast and its updates. Specific to this update, we are at the halfway stage of what is typically considered the four month monsoon (this too needs revision, as April and May rains were not the usual ‘unseasonal’ passing showers). However, any downward revision of the rainfall average for August and September ought to be an overall downward revision of the season, particularly as June-July have seen very uneven rain.
Consider the highlights of the updated monsoon forecast:
* Quantitatively, the rainfall over the country as a whole during the second half of the season (August to September) is likely to be 84% of LPA with a model error of ±8%.
* The rainfall during August is likely to be 90 ± 9% of LPA as was forecasted in June.
* The season (June to September) rainfall over the country as a whole is likely to be 88% of LPA with a model error of ±4% as was forecasted in June.
 We make our criticism constructively, for a significant amount of the material India Climate Portal puts out through our website and our twitter account is taken from the public products released by IMD, ISRO and the Ministry of Earth Sciences, and we fully appreciate the quality of work and commitment of these agencies.
We make our criticism constructively, for a significant amount of the material India Climate Portal puts out through our website and our twitter account is taken from the public products released by IMD, ISRO and the Ministry of Earth Sciences, and we fully appreciate the quality of work and commitment of these agencies.
The national mean rainfall (“country as a whole”, as the IMD forecasts call it) must be abandoned as it does not represent the meteorological diversity of a very large country. Each of the 36 met sub-divisions is affected in different ways by the El Nino Southern Oscillation, the Indian Ocean dipole, the Madden-Julian Oscillation and other hemispheric phenomena.
There is no need for this simplification, which in fact achieves the opposite of timely accuracy.
The media in particular (television and radio, print, online) look for an overall message and, without guidance from authorities, picks up ‘top line’ messages that are of little or no use at the district and taluka level, and also for towns and cities. The question for IMD is rather: how will variability in monsoon together with the strengthening El Nino affect local outlooks for August to October. That is why we advocate monthly outlooks for the 36 met sub-divisions, to begin in May and to run until October (that is, half the year and not a third of the year), primarily to prepare local administrations for all possible scenarios.
There is no reason why this cannot be the approach. The Ministry of Earth Sciences coordinates the observation network (satellites included, and our agencies ISRO and NRSC are heavily involved), the IMD uses these data together with a very extensive network of weather stations all over India. The output is excellent quality and in the public domain. Because the meteorological services in India have historically been designed to aid and guide agriculture and cultivation, the agri-met bulletins, alerts and products are copious. Hence IMD/MoES listens to the needs of the agricultural departments and, more recently, disaster management agencies. Unfortunately, the interface with public is still minimal, which this central government can also easily remedy.



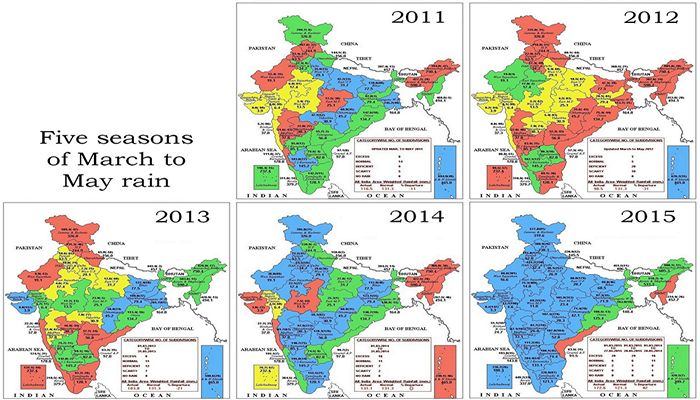

 Whether the monsoon starts off on time, whether the June, July, August and September rainfall averages are met, and whether the seasonal pattern of the monsoon is maintained are expectations that must now be set aside.
Whether the monsoon starts off on time, whether the June, July, August and September rainfall averages are met, and whether the seasonal pattern of the monsoon is maintained are expectations that must now be set aside.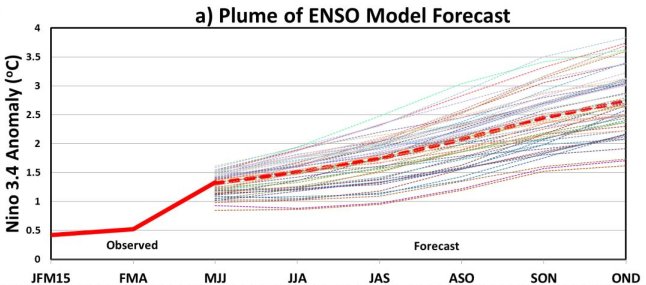

 Every one of Haryana’s 21 districts received excess rain for the period 1 March to 30 April 2015. As these rains have destroyed crops, including food staples, the need to compensate the affected farming families is now paramount. Relief and support are only useful when they are arrive quickly, and unlike administrative conditions two generations ago, state governments and district collectors today can consult data around the clock about conditions in districts and blocks.
Every one of Haryana’s 21 districts received excess rain for the period 1 March to 30 April 2015. As these rains have destroyed crops, including food staples, the need to compensate the affected farming families is now paramount. Relief and support are only useful when they are arrive quickly, and unlike administrative conditions two generations ago, state governments and district collectors today can consult data around the clock about conditions in districts and blocks.


 Our coverage of the ‘mausam’, the Indian summer monsoon of 2015, has begun. The unseasonal rains of March and April, which have proved so destructive to farmers, have shown why the conventional monsoon season must be widened. You will find all
Our coverage of the ‘mausam’, the Indian summer monsoon of 2015, has begun. The unseasonal rains of March and April, which have proved so destructive to farmers, have shown why the conventional monsoon season must be widened. You will find all  From the first week of June 2014 until the middle of September 2014, there have been floods and conditions equivalent to drought in many districts, and for India the tale of monsoon 2014 comes from a reading of individual districts, not from a national ‘average’ or a ‘cumulative’. [
From the first week of June 2014 until the middle of September 2014, there have been floods and conditions equivalent to drought in many districts, and for India the tale of monsoon 2014 comes from a reading of individual districts, not from a national ‘average’ or a ‘cumulative’. [

