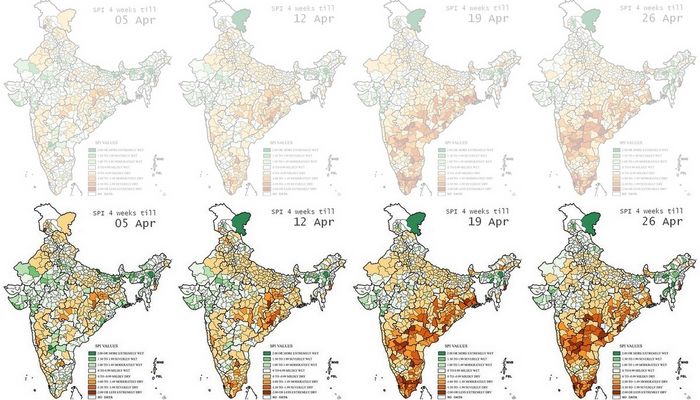
Monsoon rains in Vidarbha better than the rains in Konkan Maharashtra? How can this be possible? Especially when the average rainfall for the seven districts of Konkan Maharashtra, over 1 June to 9 August, is 1,812 mm and the average rainfall for the 11 districts of Vidarbha Maharashtra is 427 mm over the same period?
The measure that we are piloting is not based on the cumulative totals, for each district during each week of monsoon 2017, but for how adequate the rainfall has been over each week. What does that mean? Maharashtra’s Konkan region receives over four times the amount of rainfall that Vidarbha does. This does not mean that Vidarbha is more ‘rain poor’ than Konkan Maharashtra. The two meteorological regions are different just as their agro-ecologies, soils, water retention structures and flora are different.
Because of this difference, it is more useful to us to judge how adequate rainfall has been over any given period of measurement. We have taken a week because that is what we have data for, as provided by the Department of Hydrometeorology or the Department of Agricultural Meteorology of the India Meteorological Department, Ministry of Earth Sciences.
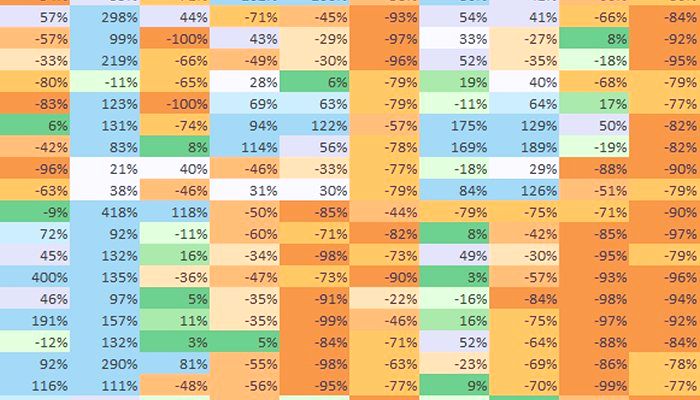
If you examine the cumulative totals – this means the running totals which from one week to the next carry over extras or deficits – the picture is as follows. One district only (Mumbai City) of the seven in Konkan Maharashtra is deficit (with -22%), all the rest being ‘normal’ in the range of -19% to +22%. The cumulative measurement picture for Vidarbha is this: only four out of the 11 districts (Buldana, Gadchiroli, Nagpur and Wardha) are ‘normal’ and in the range of -15% to -19%. The remaining seven are ‘deficit’ in the range of -23% to -36% (Amravati and Yavatmal being the lowest).
The weakness of the cumulative measure is that it ‘carries forward’ deficits and surpluses. A deficit in weeks 3 and 4 can be ‘made up’ for by better rains in week 5 and 6. But when rain in weeks 3 and 4 are important for a particular phase of a crop’s growth, the surplus that follows is of little use.
That’s where this pilot measure, what I have called the ‘rainfall adequacy index’, comes in. It indexes normalcy and variation from normalcy, plus or minus, and so records how adequate every week has been for the district. Using this method, we find that among Maharashtra’s meteorological regions, it is Vidarbha that has done best over 1 June to 9 August, followed by Konkan Maharashtra, then by Madhya Maharashtra and with Marathwada last.
The footnote is that the three districts with the best ‘rainfall adequacy index’ over this period are, in order, Sindhudurg, Nagpur and Wardha. The three districts with the worst index are Osmanabad, Nashik and both Thane and Palghar.
– Rahul Goswami