Launched in 2009 with the support of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), Government of India, the Centre of Climate Change Research (CCCR) is part of the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) in Pune, Maharashtra. The CCCR focuses on development of new climate modelling capabilities in India and South Asia to address issues concerning the science of climate change.
The Centre has now released an ‘Interim Report on Climate Change over India’ which is intended to provide a brief overview of: (a) updated assessment of observed climate change over India, (b) future climate projections over India, (c) development of the IITM Earth System Model to better understand and quantify climate change and its regional impacts. The three topics, which are among the core research activities of the CCCR at IITM, have been presented as three chapters in this Interim Report, and an updated report is planned to be submitted later next year.
Assessments of impacts of climate change and future projections over the Indian region, have so far relied on a single regional climate model (RCM) such as the PRECIS RCM of the Hadley Centre, UK. While these assessments have provided inputs to various reports (INCCA 2010; NATCOMM2 2012), it is important to have an ensemble of climate projections drawn from multiple RCMs due to large uncertainties in regional-scale climate projections. Ensembles of multi-RCM projections driven under different perceivable socio-economic scenarios are required to capture the probable path of growth, and provide the behavior of future climate and impacts on various biophysical systems and economic sectors dependent on such systems. [The full report is available here (pdf).]
The Centre for Climate Change Research, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (CCCR-IITM) has generated an ensemble of high resolution downscaled projections of regional climate and monsoon over South Asia until 2100 for the Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (IPCC) using a RCM (ICTP-RegCM4) at 50 km horizontal resolution, by driving the regional model with lateral and lower boundary conditions from multiple global atmosphere-ocean coupled models from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5). The future projections are based on three Representation Concentration Pathway (RCP) scenarios (viz., RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP8.5) of the IPCC.
These high-resolution downscaled projections of regional climate over South Asia are generated as part of the International Programme called Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment (CORDEX) sponsored by the World Climate Research Programme. This chapter provides a synthesis of results from the CORDEX South Asia multi-RCM outputs, that allows us to interpret the strengths and limitations of future regional climate projections over India. This information is useful to reduce uncertainty of impact assessment estimates to an extent and provide a pan-Indian regional assessment for informed policy-making.
Key points
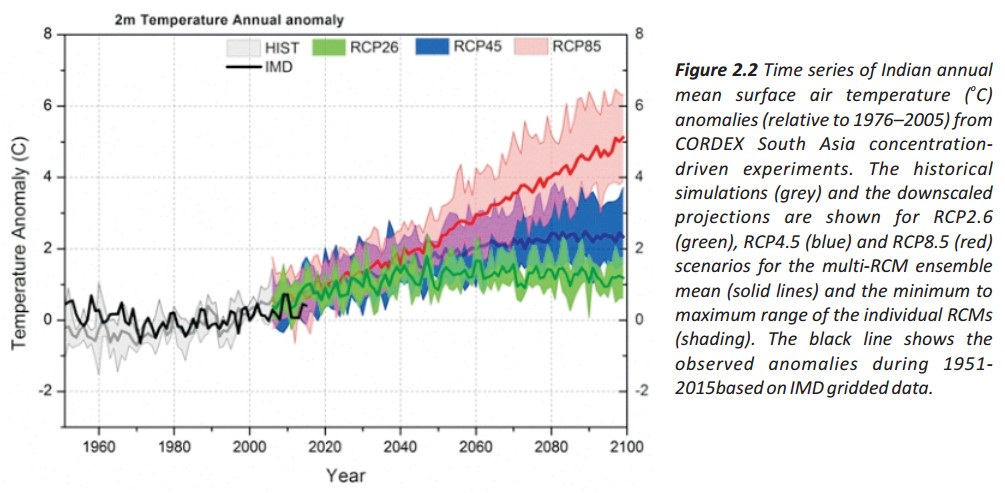
⊗ The all India mean surface air temperature change for the near-term period 2016–2045 relative to 1976–2005 is projected to be in the range of 1.08°C to 1.44°C, and is larger than the natural internal variability. This assessment is based on a reliability ensemble average (REA) estimate incorporating each RCM performance and convergence, and is associated with less than 16% uncertainty range.
⊗ The all India mean surface air temperature is projected to increase in the far future (2066–2095) by 1.35 ± 0.23°C under RCP2.6, 2.41 ± 0.40°C under RCP4.5 and 4.19 ± 0.46°C under RCP8.5 scenario respectively. These changes are relative to the period 1976–2005. The semi-arid north-west and north India will likely warm more rapidly than the all India mean.
 ⊗ Monthly increase in all India mean surface air temperature based on REA estimate is relatively higher during winter months than in the summer monsoon months throughout the 21st century under the three RCP scenarios.
⊗ Monthly increase in all India mean surface air temperature based on REA estimate is relatively higher during winter months than in the summer monsoon months throughout the 21st century under the three RCP scenarios.
⊗ The REA changes for all India annual minimum temperature of 4.43 ± 0.34oC is more pronounced than that of 3.94 ± 0.45oC and 4.19 ± 0.46oC increases estimated for the respective annual maximum and mean temperatures respectively the end of the 21st century under RCP8.5 scenario. The models project substantial changes in temperature extremes over India by the end of the 21st century, with a likely overall decrease in the number of cold days and nights, and increase in the number of warm days and nights.
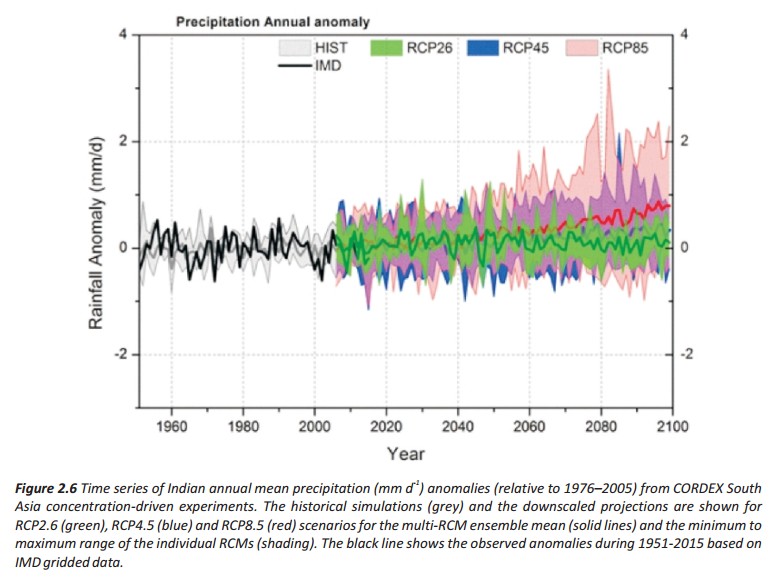
⊗ Although the all India annual precipitation is found to increase as temperature increases, the REA assessment indicates that precipitation changes throughout the 21st century remain highly uncertain.
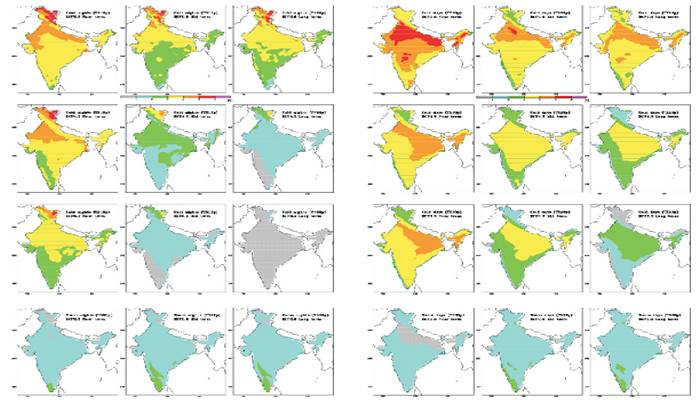
⊗ The all India annual precipitation extremes are projected to increase with relatively higher uncertainty under RCP8.5 scenario by the end of the 21st century. The downscaled projections suggest that intensification of both dry and wet seasons is expected along the west coast of India and in the adjoining peninsular region.
The multi-RCM ensemble mean annual precipitation mid-term increase exceeds 10% over the west coast and the adjoining southern parts of the Indian peninsula for RCP4.5 scenario, while in the long-term the change for this mid-scenario exceeds 20% over the south-west coast and the adjoining Kerala state. The precipitation changes are not significant over the remaining parts of India for this mid-scenario up to the mid 21st century, however in long-term increase exceed 10% over north-west and adjoining parts of the country. The long-term projected annual precipitation increase exceeds 10% over most parts of India except in Jammu and Kashmir under RCP8.5 scenario, with relatively higher increase exceeding 30% projected along the west coast of India for this high-emission scenario by the end of 21st century.