Recent reports bring positive news related to renewable energy investment and the feasibility of a 100% renewable energy future. The UN Environment Programme (UN Environment, or UNEP), the Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre, and Bloomberg New Energy Finance released a report titled ‘Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2017,’ which finds that wind, solar, biomass and waste-to-energy, geothermal, small hydro and marine sources added 138.5 gigawatts to global power capacity in 2016, up 8% from the 127.5 gigawatts added in 2015.
Recent reports bring positive news related to renewable energy investment and the feasibility of a 100% renewable energy future. The UN Environment Programme (UN Environment, or UNEP), the Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre, and Bloomberg New Energy Finance released a report titled ‘Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2017,’ which finds that wind, solar, biomass and waste-to-energy, geothermal, small hydro and marine sources added 138.5 gigawatts to global power capacity in 2016, up 8% from the 127.5 gigawatts added in 2015.
The report indicates that as the cost of clean technology continues to fall, the world added record levels of renewable energy capacity in 2016, at an investment level 23% lower than the previous year. According to UN Environment, the added generating capacity roughly equals that of the world’s 16 largest existing power producing facilities combined.
Global Trends in Renewable Energy Investment 2017, published on April 6th by UN Environment, the Frankfurt School-UNEP Collaborating Centre, and Bloomberg New Energy Finance, finds that all investments in renewables totaled $241.6 billion (excluding large hydro). These investments added 138.5 gigawatts to global power capacity in 2016, up 9 per cent from the 127.5 gigawatts added the year before.
Investment in renewables capacity was roughly double that in fossil fuel generation; the corresponding new capacity from renewables was equivalent to 55 per cent of all new power, the highest to date. The proportion of electricity coming from renewables excluding large hydro rose from 10.3 per cent to 11.3 per cent. This prevented the emission of an estimated 1.7 gigatons of carbon dioxide.
The total investment was $241.6 billion (excluding large hydro), the lowest since 2013. This was in large part a result of falling costs: the average dollar capital expenditure per megawatt for solar photovoltaics and wind dropped by over 10 per cent.

 Solar
Solar 




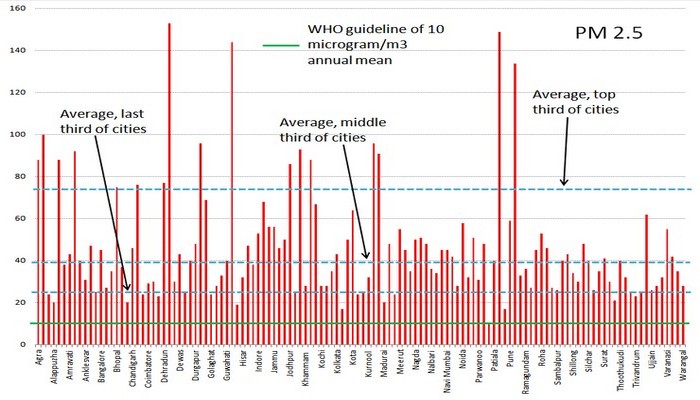
 We must question the profligacy that the Goyal team is advancing in the name of round the clock, reliable and affordable electricity to all. To do so is akin to electoral promises that are populist in nature – and which appeal to the desire in rural and urban residents alike for better living conditions – and which are entirely blind to the environmental, health, financial and behavioural aspects attached to going ahead with such actions. In less than a fortnight, prime minister Narendra Modi (accompanied by a few others)
We must question the profligacy that the Goyal team is advancing in the name of round the clock, reliable and affordable electricity to all. To do so is akin to electoral promises that are populist in nature – and which appeal to the desire in rural and urban residents alike for better living conditions – and which are entirely blind to the environmental, health, financial and behavioural aspects attached to going ahead with such actions. In less than a fortnight, prime minister Narendra Modi (accompanied by a few others)