
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) on 16 April had issued its first long range forecast for the 2018 South-West Monsoon season, which the IMD has historically taken to be 1 June to 30 September. The IMD had said that the “monsoon seasonal rainfall is likely to be 97% of the Long Period Average with a model error of ± 5%”. The IMD had also said that its forecast “suggests maximum probability for normal monsoon rainfall (96%-104% of the long period average) and low probability for deficient rainfall during the season”.
In early June, the IMD will issue its second long range forecast for the 2018 monsoon. Until then, we have studied three of the more reliable (in our view) international multi-model ensemble forecasts for the monsoon. What are ensemble forecasts? Each consists of several separate forecasts (some ensembles use 50) forecasts made by the same computer model – these are run on super-computers such as the High Performance Computer System of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (one is at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology in Pune with 4.0 petaflops capacity and the other at the National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting in Noida with 2.8 petaflops capacity).

The MME forecast is based on estimated precipitation anomalies relative to the period 1993-2016, based on initial conditions calculated at the beginning of May 2018. Four blocks of three months each.
The separate forecasts that make up one ensemble are all activated from the same starting time. The starting conditions for each differ from each other to account as far as possible for the staggering number of climatological, atmospheric, terrestrial and oceanographic variables that affect and influence our monsoon. The differences between these ensemble members tend to grow as the forecast travels two, three, four and more months ahead of the present.
We have considered the ensemble forecasts for the 2018 monsoon of the Multi-Model Ensemble (MME) of the USA National Centers for Environmental Prediction, the NOAA Climate Prediction Center and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecast (ECMWF). In this order, we find that the MME is optimistic, the NOAA CPC is largely neutral and the ECMWF forecast is somewhat pessimistic. The forecasting periods are in blocks of three months.
Here are the details:
(1) The MME forecast, precipitation anomalies relative to the period 1993-2016, based on initial conditions calculated at the beginning of May 2018.
June July August (JJA) – west coast and Konkan, coastal Andhra Pradesh and Odisha, West Bengal, part of the North-East, the entire upper, middle and lower Gangetic region (Uttarakhand, Himachal, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Jharkhand), Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Telengana to have up to +1 mm/day. Rest of India other than Gujarat (-0.5 mm/day) normal.
July August September (JAS) – Gujarat to have up to -1 mm/day, Rajasthan up to -0.5 mm/day, Sikkim, Brahmaputra valley and Arunachal Pradesh up to -0.5 mm/day. Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand up to +0.5 mm/day, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and West Bengal up to +0.5 mm/day. Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu up to -0.5 mm/day.
August September October (ASO) – Gujarat up to -0.5 mm/day. Tamil Nadu up to -1 mm/day. Kerala and adjacent Karnataka up to -0.5 mm/day. Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal up to +1 mm/day. Tripura, Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh up to +0.5 mm/day
September October November (SON) – Tamil Nadu, Kerala and adjacent Karnata up to -1 mm/day. Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand up to +0.5 mm/day.
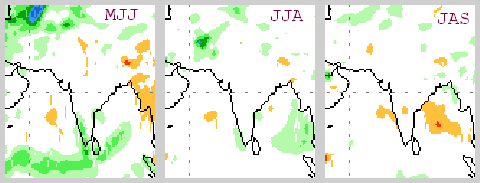
The NOAA CPC forecast is based on estimated seasonal precipitation anomalies using initial conditions of 30 April 2018 to 9 May 2018. Three blocks of three months each.
(2) The NOAA CPC forecast, seasonal precipitation anomalies using initial conditions of 30 April 2018 to 9 May 2018.
May June July (MJJ) – for most of India a normal reading (+0.5 to -0.5 mm/day fluctuation) and for the west coastal, Konkan, Kerala, south Tamil Nadu and coastal Andhra Pradesh areas variation of up to +1.5 mm/day.
June July August (JJA) – for most of India a normal reading (+0.5 to -0.5 mm/day fluctuation).
July August September (JAS) – normal for most of India. Some areas in the central Deccan plateau, on the west coast and east coast variation of up to -1 mm/day.

The ECMWF forecast is based on estimated mean precipitation anomaly based on climate period data of 1993-2016 and initial conditions as on 1 May 2018. Four blocks of three months each.
(3) The ECMWF forecast, mean precipitation anomaly based on climate period data of 1993-2016 and initial conditions as on 1 May 2018.
June July August (JJA) – all of the southern peninsula and part of the Deccan region (Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, part of Telengana up to -100 mm for the period. West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh up to +100 mm for the period.
July August September (JAS) – all of the southern peninsula and the Deccan region – Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, part of Telengana and Maharashtra up to -100 mm for the period.
August September October (ASO) – Maharashtra, Telegana, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka up to -100 mm for the period.
September October November (SON) – Central and western India, eastern states and entire Gangetic region up to -50 mm for the period.
Rahul Goswami
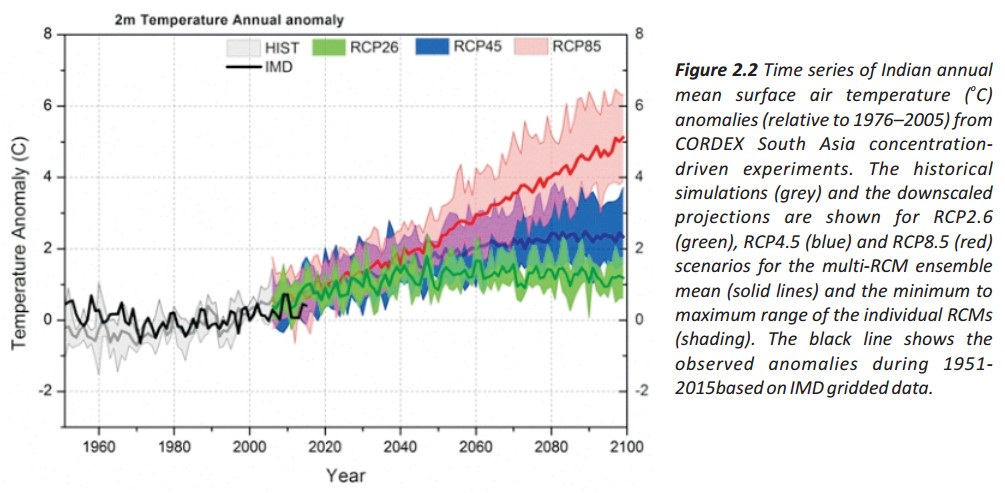
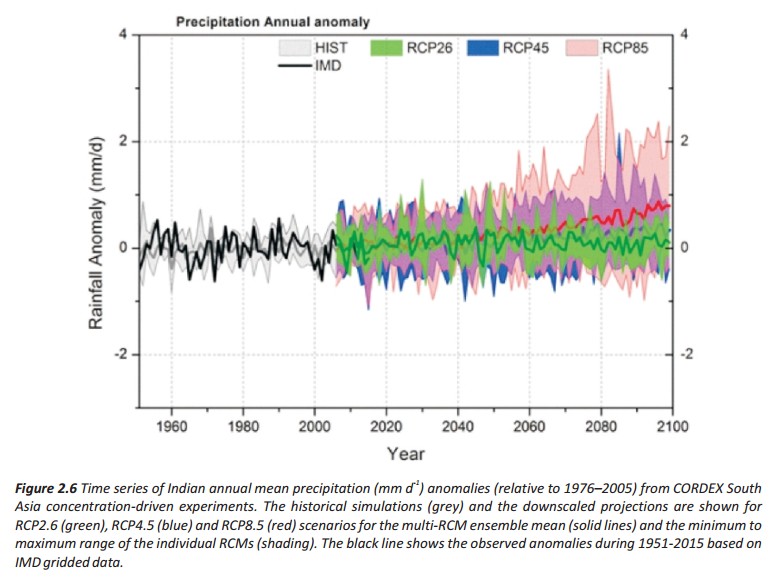 ⊗ Monthly increase in all India mean surface air temperature based on REA estimate is relatively higher during winter months than in the summer monsoon months throughout the 21st century under the three RCP scenarios.
⊗ Monthly increase in all India mean surface air temperature based on REA estimate is relatively higher during winter months than in the summer monsoon months throughout the 21st century under the three RCP scenarios.
