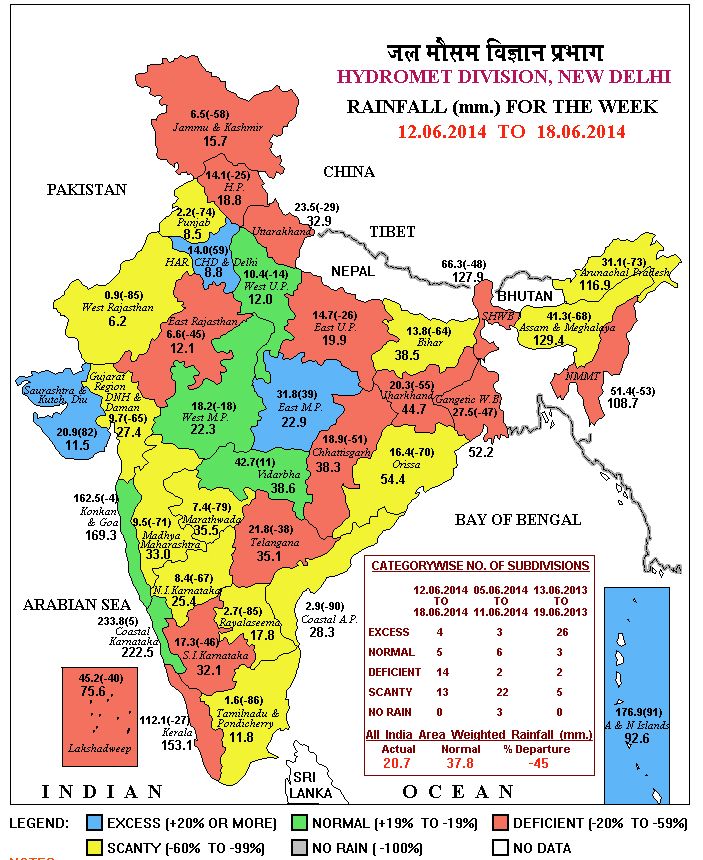
 We urge the Ministry of Earth Sciences, the India Meteorology Department and the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting to cease the use of a ‘national’ rainfall average to describe the progress of monsoon 2014. This is a measure that has no meaning for cultivators in any of our agro-ecological zones, and has no meaning for any individual taluka or tehsil in the 36 meteorological sub-divisions. What we need to see urgently adopted is a realistic overview that numerically and graphically explains the situation, at as granular a level as possible.
We urge the Ministry of Earth Sciences, the India Meteorology Department and the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting to cease the use of a ‘national’ rainfall average to describe the progress of monsoon 2014. This is a measure that has no meaning for cultivators in any of our agro-ecological zones, and has no meaning for any individual taluka or tehsil in the 36 meteorological sub-divisions. What we need to see urgently adopted is a realistic overview that numerically and graphically explains the situation, at as granular a level as possible.
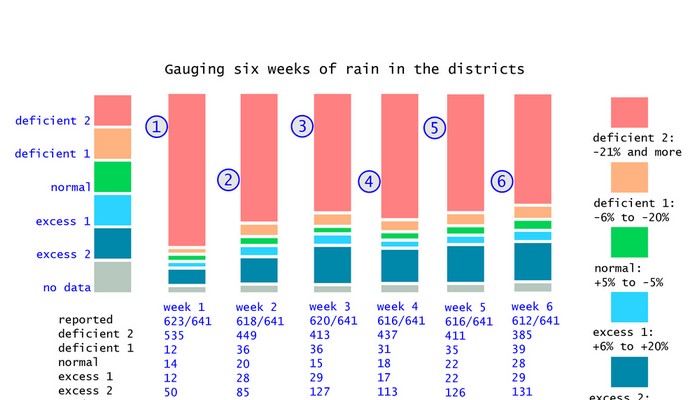
Using a revised categorisation of rainfall sufficiency levels (the method and the reasoning is available here) we find that for the fifth and sixth weeks of monsoon, there has been a small improvement which does not lower the high likelihood of drought conditions becoming prevalent in districts and scarcity of water for our settlements. The full-size chart is available here as an image, and explains in detail the rainfall that districts are reporting.
The fifth monsoon week is 03 to 09 July 2014 and the sixth monsoon week is 10 to 16 July 2014. There has been a small addition to the revised normal rainfall category (-5% to +5%), rising from 18 districts recording normal rainfall in the 4th week to 22 in the 5th and 28 in the 6th. There has also been an improvement in the number of districts recording deficit-2 levels of rainfall (-21% and more) with 437 in the 4th week, 411 in the 5th week and 385 in the 6th week. For the remainder of July the likelihood of more rainfall in the districts that have recorded normal or excess-1 (+6% to +20%) is small, according to the available forecasts, and this means that monsoon 2014 will begin August with far fewer districts registering normal rainfall than they should at this stage.