Whether or not the USA, Europe, the Western world, the industrialised Eastern world (China, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan), adhere to or not their paltry promises about being more responsible concerning the factors that lead to climate change, is of very little concern to us. We have never set any store by international agreements on climate change.
This year will see the twenty-third conference of parties of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change and for 23 years the world and India have listened to lofty tales about simple science. In these 23 years, neither has reckless consumption been halted nor has the economic model that encourages such reckless consumption been questioned by the conference of parties. As long as they do not, inter-governmental agreements are useless.
That is why we find unnecessary and pointless the hand-wringing that has taken place about the decision of the government of the USA to exit what is called the ‘Paris Agreement’, the December 2015 document agreed to and signed by practically every country which has some fuzzy paragraphs about low-carbon economy, innovation, technology, energy and finance – all of which have very much to do with the hold of the finance capitalists and the global technocrats over the international systems of our time.
President number 45 of the USA is neither wiser than nor baser than the wisest of basest of any of his predecessors: the American political system has to do entirely with the desire to dominate other countries. Number 45’s manner may be irksome, but through him speaks the American finance capital, its bloatsome defence industry and its insensate technology industry.
We do not expect the chiefs of the Western countries, the so-called major powers of the European Union, and their allies such as Japan and Australia to do any less. They are no different. We do not think any of them, their armies of bland advisers, their bankers and the brigades of industrialists great and petty who crowd their corridors of governance have read, much less reflected, on the lambent wisdom of our civilisation.
Many centuries ago, in the section of the Digha Nikaya, or Collection of Long Discourses, called Samannaphala Sutta, or the Fruits of the Contemplative Life, it was written that there are those who are addicted to debates and shout: “You understand this doctrine and discipline? I’m the one who understands this doctrine and discipline. How could you understand this doctrine and discipline? You’re practicing wrongly. I’m practicing rightly. I’m being consistent. You’re not. What should be said first you said last. What should be said last you said first. What you took so long to think out has been refuted. Your doctrine has been overthrown. You’re defeated. Go and try to salvage your doctrine; extricate yourself if you can!”
And this is how we view what are called climate negotiations, between the experts of countries. We care not for the arguments of number 45 of the USA, for what many in the world in the last week have protested as being absurd – it undermines economy, it takes away jobs, it is unfair, it is disadvantageous to us, and so on – is what they cheer and support their own countries for in areas where they stand to gain, such as trade (to sell cheap and useless goods), technology (to enslave and control), finance (to spin webs of debt), processes of modernisation (to homogenise cultures so that ever more ‘markets’ come into being).
We in India need no such instruction. But we must guard against our philosophies being swept away by these agreements, these grand comities of nations, the barrage of numerics and scientifics that are invented to display to us what a threat we are should we not emulate the West and its ways. We must guard against our own who prefer the baubles of post-industrial society to the intellectual and spiritual riches of our civilisation, and who seek to infest India with the same technological and ‘modern’ wares that so entranced the West and doomed its folk. This has very little to do with climate and its change and very much more to do with our Indic sciences and their worth, our conduct and our duty to Punyabhoomi Bharat.
– Rahul Goswami
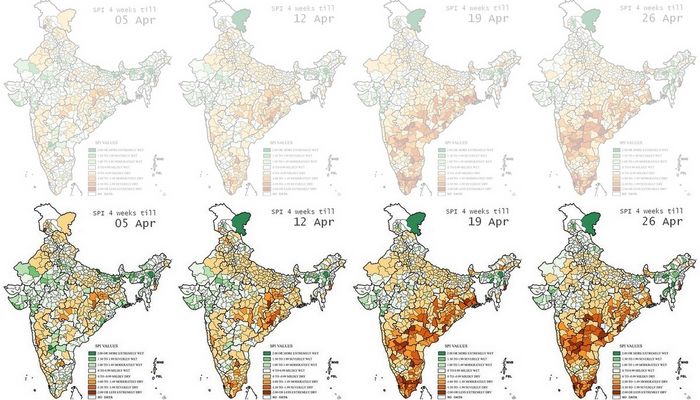



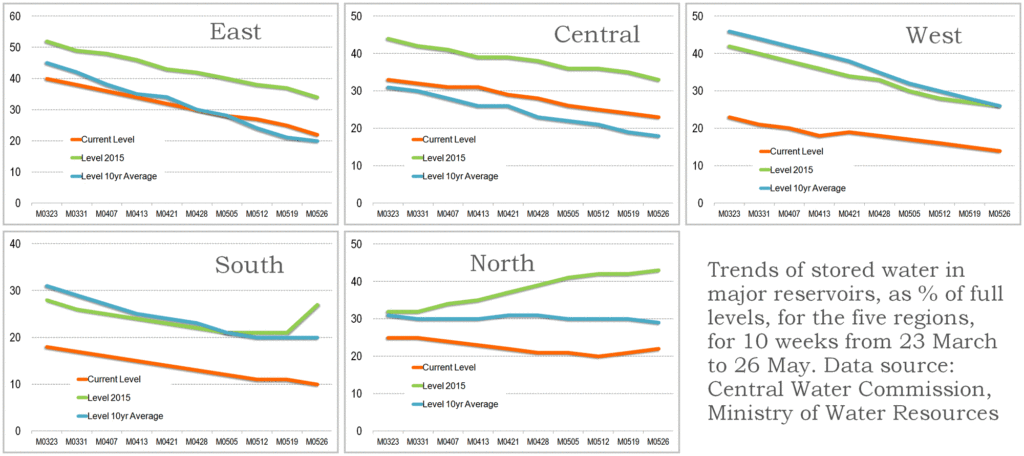
 By the end of the first week of April 2017, the most current and reliable indicator for stored water in south India showed how dire the situation has become. And the South-West monsoon is still about eight weeks away. The weekly data sheet on the stored water quantities in the 91 major reservoirs of India, which is maintained and released by the Central Water Commission, has in the 6 April 2017 release shown the scale of the water emergency.
By the end of the first week of April 2017, the most current and reliable indicator for stored water in south India showed how dire the situation has become. And the South-West monsoon is still about eight weeks away. The weekly data sheet on the stored water quantities in the 91 major reservoirs of India, which is maintained and released by the Central Water Commission, has in the 6 April 2017 release shown the scale of the water emergency.


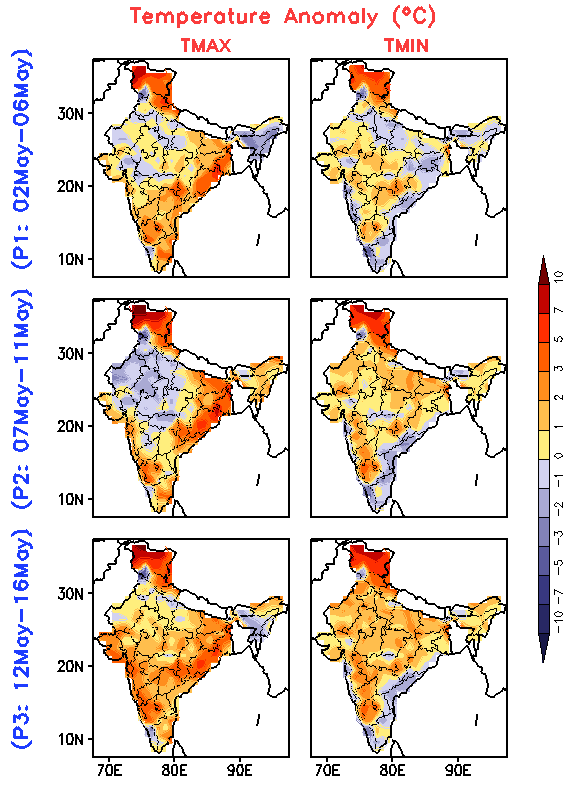
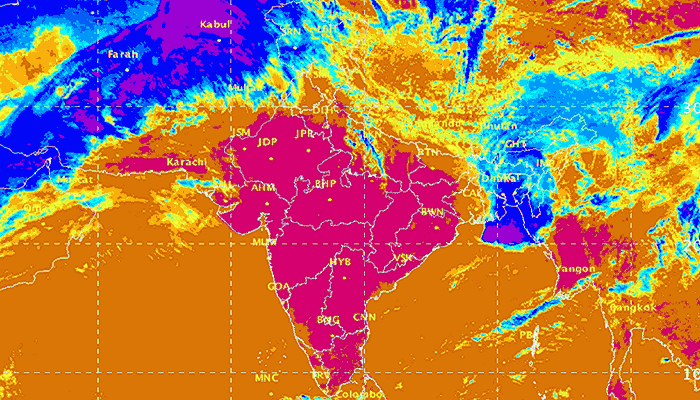
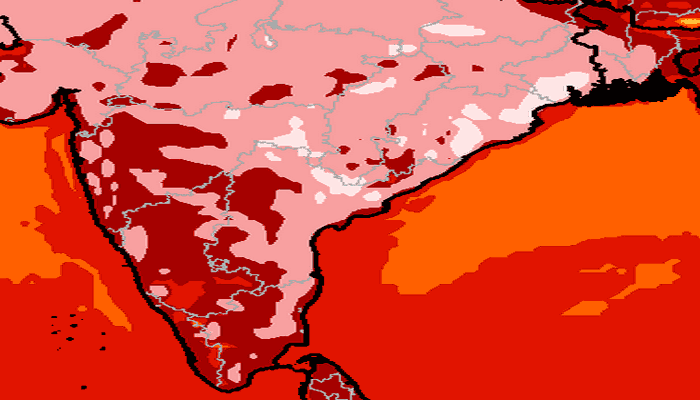 The heat outlook for the first half of May, which was released by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) on 02 May, calls for immediate attention and preparation on all fronts.
The heat outlook for the first half of May, which was released by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) on 02 May, calls for immediate attention and preparation on all fronts.