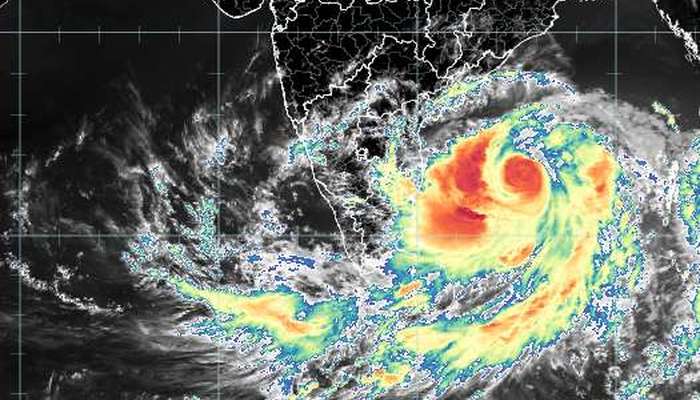

Update: Cyclone Fani will make landfall on the coast on 3 May. Depending on whether the Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm (IMD’s classification) gains more speed over the Bay of Bengal, Fani could cross the coast as early as 1000 hours on 3 May.
Based on the weather charts released by IMD and corroborated by the climatological forecasts produced by the World Meteorological Organisation’s members, Fani will cross the coast between Kakinada, East Godavari district, Andhra Pradesh, and Puri, district Puri, Odisha, which is about 60 km south of Bhubaneshwar.
Previously: The India Meteorological Department has issued a forcast for and warning about a cyclonic storm which as of today (27 Apri) is a low pressure area lying over the East Equatorial Indian Ocean and adjoining south-east Bay of Bengal.
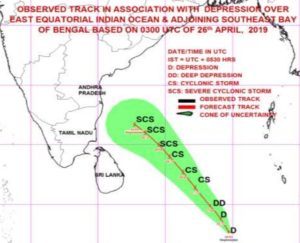 It is already intensifying into a depression over the East Equatorial Indian Ocean and adjoining central parts of the southern Bay of Bengal and will further intensify into a cyclonic storm. Thereafter the storm is forecast to move north-westwards along and off the east coast of Sri Lanka near the north Tamil Nadu coast on 30 April.
It is already intensifying into a depression over the East Equatorial Indian Ocean and adjoining central parts of the southern Bay of Bengal and will further intensify into a cyclonic storm. Thereafter the storm is forecast to move north-westwards along and off the east coast of Sri Lanka near the north Tamil Nadu coast on 30 April.
The IMD has already issued warning to fishermen about strong winds. Wind speed reaching 45-55 kmph gusting to 65 kmph over East Equatorial Indian Ocean and adjoining central parts of the southern Bay of Bengal are already being recorded. Gale wind speeds will be reached of 65-75 kmph gusting to 85 kmph over the south-west Bay of Bengal and adjoining Equatorial Indian Ocean by 27 April.
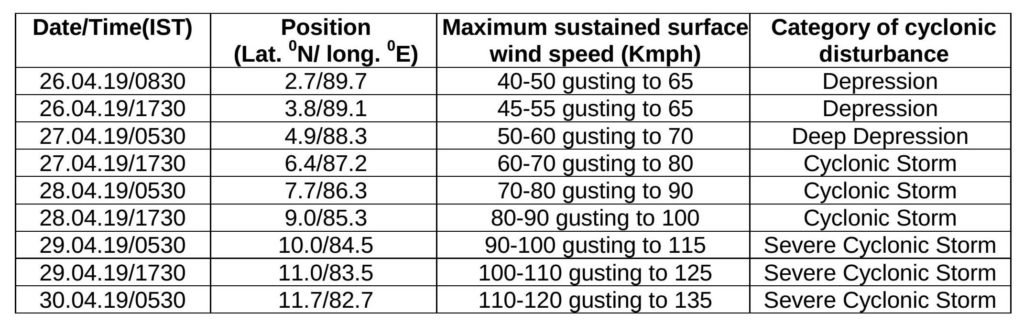 Thereafter 80-90 kmph gusting to 100 kmph over the south-west Bay of Bengal and adjoining Equatorial Indian Ocean and along and off the Sri Lankan coast on 28 April and 90-100 kmph gusting to 115 kmph over the south-west Bay of Bengal, along and off the Sri Lankan coast and off the Tamil Nadu and Puducherry coast on 29 April. The sea condition will be very rough in all these areas.
Thereafter 80-90 kmph gusting to 100 kmph over the south-west Bay of Bengal and adjoining Equatorial Indian Ocean and along and off the Sri Lankan coast on 28 April and 90-100 kmph gusting to 115 kmph over the south-west Bay of Bengal, along and off the Sri Lankan coast and off the Tamil Nadu and Puducherry coast on 29 April. The sea condition will be very rough in all these areas.
There will be light to moderate rainfall at many places with heavy rainfalls at isolated places in north coastal Tamil Nadu on 30 April and 1 May and over Kerala on 29 and 30 April. Light to moderate rainfall at many places with heavy rainfall at isolated places is also very likely over south coastal Andhra Pradesh on these dates.

 By the end of the first week of April 2017, the most current and reliable indicator for stored water in south India showed how dire the situation has become. And the South-West monsoon is still about eight weeks away. The weekly data sheet on the stored water quantities in the 91 major reservoirs of India, which is maintained and released by the Central Water Commission, has in the 6 April 2017 release shown the scale of the water emergency.
By the end of the first week of April 2017, the most current and reliable indicator for stored water in south India showed how dire the situation has become. And the South-West monsoon is still about eight weeks away. The weekly data sheet on the stored water quantities in the 91 major reservoirs of India, which is maintained and released by the Central Water Commission, has in the 6 April 2017 release shown the scale of the water emergency.









